STACK AND QUEUES IN PYTHON:
1. STACK:
A stack is a fundamental data structure in computer science that follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle. It's like a collection of items stacked on top of each other, where the last item added is the first one to be removed.( W3 school) You can think of a stack like a stack of plates: you add plates to the top of the stack and remove them from the top.
In Python, you can implement a stack using a list, and there's also the deque class from the collections module that provides efficient methods for stack operations.
 |
| javatpoint |
EXAMPLE:
# Create a stack
stack = Stack()
# Push items onto the stack
stack.push(10)
stack.push(20)
stack.push(30)
# Pop items from the stack
print(stack.pop()) # Output: 30
print(stack.pop()) # Output: 20
# Peek at the top item
print(stack.peek()) # Output: 10
# Check if the stack is empty
print(stack.is_empty()) # Output: False
# Get the size of the stack
print(stack.size()) # Output: 1
USING LIST IMPLEMENT STACK:
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def push(self, item):
self. items.append(item)
def pop(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self. items.pop()
def peek(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.items[-1]
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.items) == 0
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
STACK OPERATION:
1. Push (Insertion):
Pushing an element onto the stack adds it to the top.
EXAMPLE:
stack = Stack()
stack.push(10)
stack.push(20)
stack.push(30)
2. Pop (Deletion):
Popping an element removes the top element from the stack and returns it.
EXAMPLE:
top_element = stack.pop() # Returns 30
3. Peek (Top Element):
Peeking at the top element returns the element without removing it.
EXAMPLE:
top_element = stack.peek() # Returns 20
4. Check Empty:
Checking if the stack is empty returns `True` if the stack is empty, otherwise `False`.
EXAMPLE:
is_empty = stack.is_empty() # Returns False
5. Size:
Getting the stack size returns the number of elements in the stack.
EXAMPLE:
stack_size = stack.size() # Returns 2
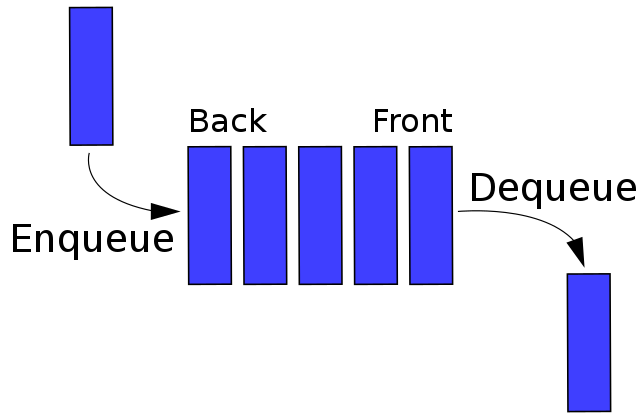
2. QUEUES:
A queue is a fundamental data structure that follows the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle. In a queue, the first element added is the first one to be removed. Think of a queue like people waiting in line—those who arrive first are served first.
QUEUE OPERATIONS:
1. Enqueue (Insertion):
Enqueuing an element adds it to the back (end) of the queue.
2. Dequeue (Deletion):
Dequeuing an element removes the front (first) element from the queue.
3. Front:
The front operation returns the element at the front of the queue without removing it.
4. Rear:
The rear operation returns the element at the back of the queue without removing it.
5. Check Empty:
Checking if the queue is empty returns `True` if the queue is empty, otherwise `False`.
6. Size:
Getting the queue size returns the number of elements in the queue.
Using a List to Implement a Queue:
EXAMPLE:
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def enqueue(self, item):
self. items.append(item)
def dequeue(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self. items.pop(0)
def front(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.items[0]
def rear(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.items[-1]
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.items) == 0
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
Using the `deque` Class:
EXAMPLE:
from collections import deque
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.items = deque()
def enqueue(self, item):
self. items.append(item)
def dequeue(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self. items.popleft()
def front(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.items[0]
def rear(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.items[-1]
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.items) == 0
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
Using the Queue:
EXAMPLE:
# Create a queue
queue = Queue()
# Enqueue elements
queue.enqueue(10)
queue.enqueue(20)
queue.enqueue(30)
# Dequeue an element
dequeued_item = queue.dequeue() # Returns 10
# Get the front and rear elements
front_element = queue.front() # Returns 20
rear_element = queue.rear() # Returns 30
# Check if the queue is empty
is_empty = queue.is_empty() # Returns False
# Get the size of the queue
queue_size = queue.size() # Returns 2





0 Comments